Checkout my twitter thread explaining how functions work in memory (stack).
Here's how functions behave in the stack (aka memory)
— Khushal Bhardwaj (@CeleronCoder) September 19, 2022
A thread 🧵#programming #DSA #ALGO #recursions #stack #memory #functions
Things to keep in mind to understand functions behavior
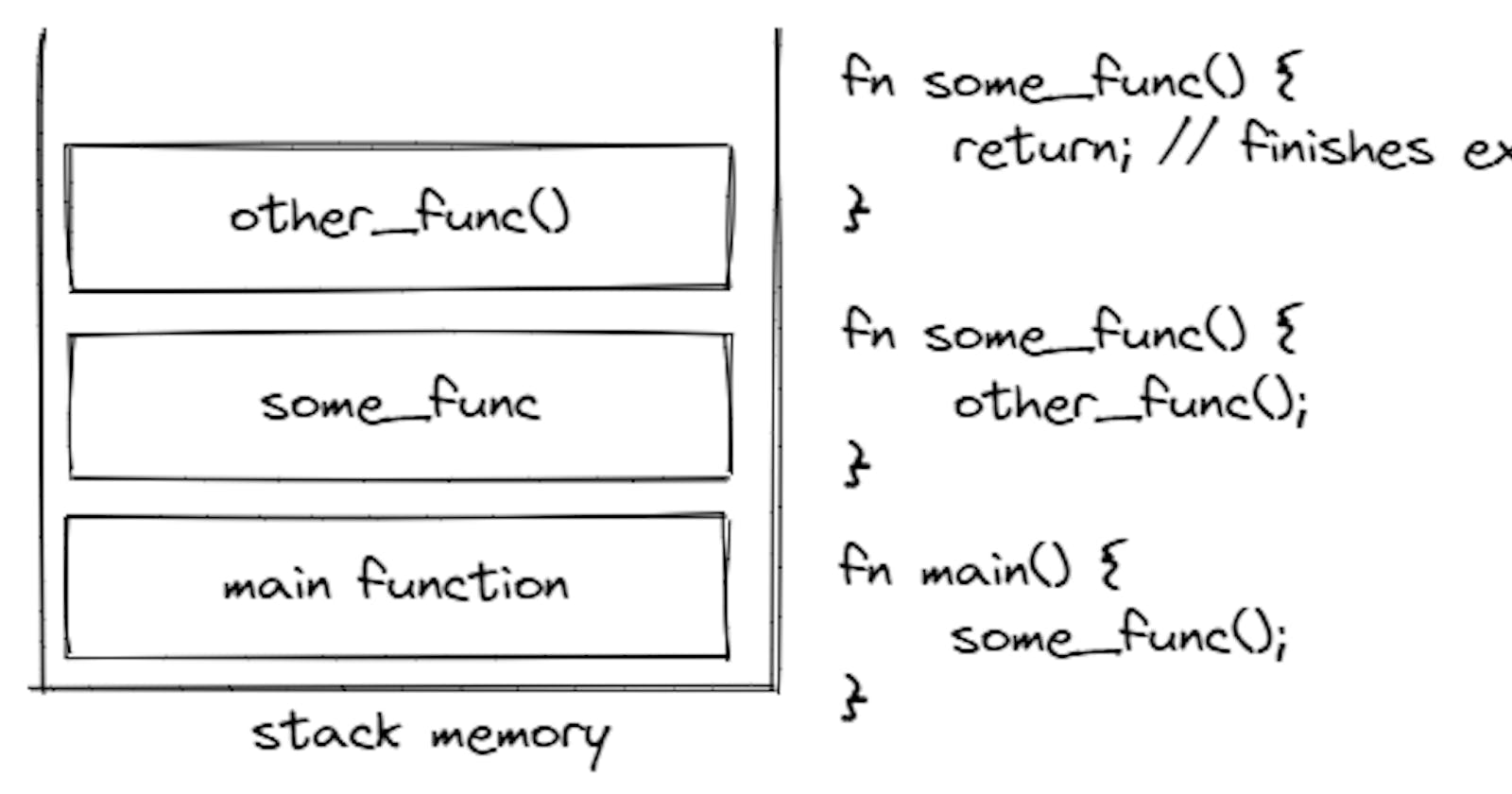
- When a function is called, it gets in the stack, and stays there until its execution.
- When the function completes executions, it gets off the stack and returns to the program flow.
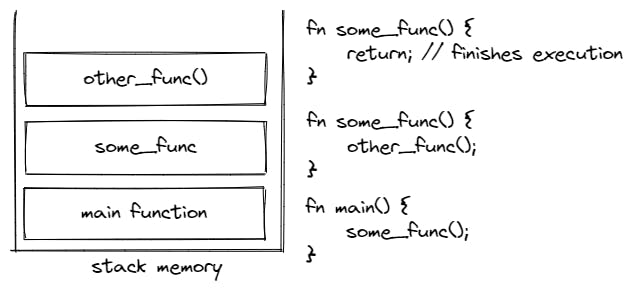
Here's a program with a main function that call some other functions and that function call some other function. As they get called, they are loaded into the memory stack.
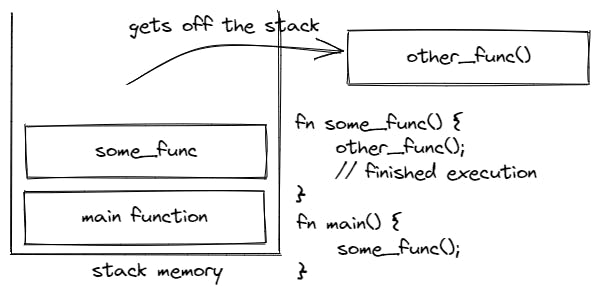
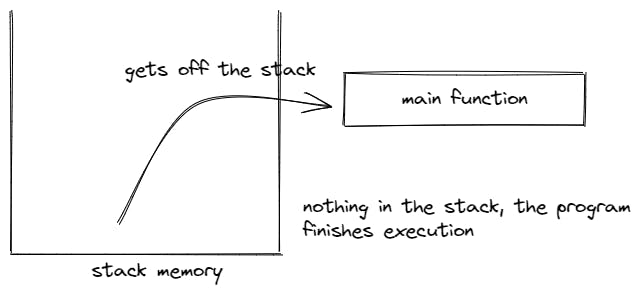
When the function, completes execution the functions gets off the stack and the program returns to the previous program flow, aka to the previous function that called that function.
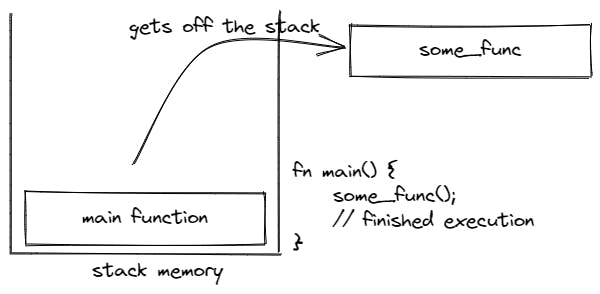
When there is nothing left in the stack, even the main function that is loaded by default, gets off the stack, the program finishes execution.
Takeaways:
- When the function is called, it is loaded on the stack with its arguments.
- When it completes execution, it gets off the stack and the program returns to its previous program flow.
If "A" function calls "B" function, "A" function will remain in the stack (and in scope also) until the "B" function returns. It means that not only the currently executing function remains in the function but also all the parent function that called it.